What is Daylight Saving Time?
Daylight Saving Time (DST), also known as daylight savings time, daylight time, or summer time, is the practice of moving clocks forward (usually by one hour) during the warmer months to ensure that darkness arrives at a later clock time. The typical implementation of DST involves advancing clocks by one hour in either late winter or spring (referred to as "springing forward") and then setting them back by one hour in the fall to return to standard time. This results in a 23-hour day in early spring and a 25-hour day in the middle of autumn.
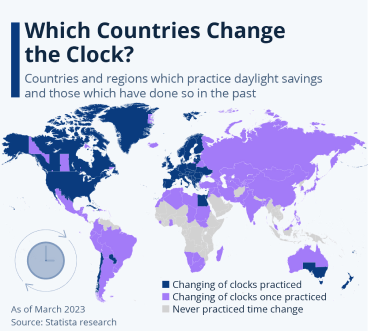
Currently, fewer than 40 percent of countries worldwide observe daylight saving time switches, even though more than 140 countries have implemented them at some point. In the United States, only two areas adhere to permanent standard/winter time: most of Arizona and Hawaii. While many U.S. states switched to summer time this weekend, Mexico opted for permanent winter time for the first time, with some regions along the U.S. border and the northern half of Baja California choosing to continue observing daylight saving time.
